Views are "lazy range combinators" that offer modified views onto other ranges. More...
 Collaboration diagram for Views:
Collaboration diagram for Views:Files | |
| file | detail.hpp |
| Auxiliary header for the views submodule . | |
Namespaces | |
| namespace | bio::ranges::views |
| The BioC++ namespace for views. | |
Classes | |
| class | bio::ranges::views::deep< underlying_adaptor_t > |
| A wrapper type around an existing view adaptor that enables "deep view" behaviour for that view. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| template<alphabet::alphabet alph_t> | |
| using | bio::ranges::views::char_conversion_view_t = decltype(std::string_view{}|bio::views::char_strictly_to< alph_t >) |
A shortcut for decltype(std::string_view{} | bio::views::char_strictly_to<alph_t>). | |
Alphabet related views | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::add_reverse_complement |
| A view that adds the reverse complement of every inner range in a range-of-ranges after the respective inner range. | |
| template<typename alphabet_type > | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::char_strictly_to |
| A view over an alphabet, given a range of characters. | |
| template<typename alphabet_type > | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::char_to |
| A view over an alphabet, given a range of characters. | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::complement |
| A view that converts a range of nucleotides to their complement. | |
| template<typename alphabet_type > | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::rank_to |
| A view over an alphabet, given a range of ranks. | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::to_char |
| A view that calls bio::alphabet::to_char() on each element in the input range. | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::to_rank |
| A view that calls bio::alphabet::to_rank() on each element in the input range. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::translate |
| A view that translates nucleotide into aminoacid alphabet with 1, 2, 3 or 6 frames. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::translate_join |
| A view that translates nucleotide into aminoacid alphabet with 1, 2, 3 or 6 frames. Input and output range are always two-dimensional. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::translate_single |
| A view that translates nucleotide into aminoacid alphabet for one of the six frames. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::trim_quality |
| A view that does quality-threshold trimming on a range of bio::alphabet::quality. | |
| template<alphabet::alphabet alphabet_type> | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::validate_char_for |
| An identity view that throws if an encountered character is not valid for the given alphabet. | |
General purpose views | |
| template<typename out_t > | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::convert |
A view that converts each element in the input range (implicitly or via static_cast). | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::interleave |
| A view that interleaves a given range into another range at regular intervals. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::pairwise_combine |
| A view adaptor that generates all pairwise combinations of the elements of the underlying range. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::persist |
| A view adaptor that wraps rvalue references of non-views. | |
| constexpr detail::repeat_fn | bio::ranges::views::repeat |
| A view factory that repeats a given value infinitely. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::repeat_n |
A view factory that repeats a given value n times. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::single_pass_input |
| A view adapter that decays most of the range properties and adds single pass behavior. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::slice |
| A view adaptor that returns a half-open interval on the underlying range. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::take_exactly |
A view adaptor that returns the first size elements from the underlying range (or less if the underlying range is shorter); also provides size information. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::take_exactly_or_throw |
A view adaptor that returns the first size elements from the underlying range and also exposes size information; throws if the underlying range is smaller than size. | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::to_lower |
| A view that converts each element to lower case. | |
| auto const | bio::ranges::views::to_upper |
| A view that converts each element to upper case. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::transform_by_pos |
| A view adaptor similar to std::views::transform. Calls the invocable with two arguments: underlying range and position. | |
| constexpr auto | bio::ranges::views::type_reduce |
| A view adaptor that behaves like std::views::all, but type erases certain ranges. | |
Views are "lazy range combinators" that offer modified views onto other ranges.
BioC++ makes heavy use of views as defined in the Ranges Technical Specification. From the original documentation: "A view is a lightweight wrapper that presents a view of an underlying sequence of elements in some custom way without mutating or copying it. Views are cheap to create and copy, and have non-owning reference semantics. [...] The big advantage of ranges over iterators is their composability. They permit a functional style of programming where data is manipulated by passing it through a series of combinators. In addition, the combinators can be lazy, only doing work when the answer is requested, and purely functional, without mutating the original data. This makes it easier to reason about your code, especially when writing concurrent programs."
See the range module for how views relate to containers and decorators.
Most views provided by BioC++ are specific to biological operations, like bio::views::trim_quality which trims sequences based on the quality or bio::views::complement which generates the complement of a nucleotide sequence. But BioC++ also provides some general purpose views.
ranges::view.bio::views.Functional and pipe notations:
Re-transform into a distinct container:
Composability:
When talking about views, two different entities are often conflated:
auto vec_view above)views::reverse and views::complement are view adaptors)The view adaptor also facilitates the piping behaviour. It is the only entity that is publicly documented and the actual view type (the range type returned by the adaptor) is considered implementation defined. The properties of the returned range are however specified and documented as part of the adaptor, see below.
An exception to this rule are views that don't work on an underlying range and can only be placed at the beginning of a pipe of operations; they do not need an adaptor, because their constructor is sufficient. This is not relevant for the documentation, though, we always document views::foo, independent of whether views::foo is the adaptor that returns the "foo type" or whether views::foo is the "foo type".
There are three view properties that are documented for a view, only if that view fulfills them:
Source-only views: Most views operate on an underlying range and return a (modified) range, i.e. they can be placed at the beginning, middle or end of a "pipe" of view operations. However, some views are limited to being at the front ("source"), e.g. std::views::single, ranges::view::concat and std::views::ints. These views are marked as "source-only" and have no urng_t column in the second table.
Sink-only views: The opposite of a source-only view. It can only be placed at the end of a pipe, i.e. it operates on views, but does not actually return a range (has no rrng_t column in the second table).
Deep views: Some views are declared as "deeps views". This means, that in case they are given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), they will apply their transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range which would be default). Most alphabet-based transformations are defined as deep, but you can use bio::views::deep to make any view (adaptor) deep. See bio::views::deep for more details.
For all views the following are documented:
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | [required] (usually) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] (usually preserved) |
| std::ranges::forward_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] (usually lost) |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | [required] (usually) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] (usually guaranteed) |
| std::ranges::view | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] (usually guaranteed) |
| std::ranges::sized_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] |
| std::ranges::common_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] |
| std::ranges::output_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost|guaranteed] |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | [required] (or not) | [preserved|lost] |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | optionally a type or concept | optionally a type or concept |
Underlying range requirements: All view adaptors that are not source-only make certain assumptions about their underlying range. The most basic assumption is that the range satisfies std::ranges::input_range, but many have stronger requirements, e.g. std::ranges::random_access_range. The concepts in the first block all build up on each other, i.e. requiring one implies requiring those above; the other concepts are mostly independent of each other. Most views also require that the underlying range satisfy std::ranges::viewable_range which means they don't accept temporary range objects other than views (because they are cheap to copy). A prominent exception to the latter is views::persist that exists exactly for this purpose. Note that these being requirements means that they are the minimal set of properties assumed. Views may very well make use of stronger properties if available.
Return range guarantees: All view adaptors that are not sink-only return a range that meets at least std::ranges::input_range and also std::ranges::view (and conversely also std::ranges::viewable_range, because all views are viewable). Most views also preserve stronger properties, e.g. std::ranges::random_access_range, but this depends on the view. Some views also add properties not present on the input range, e.g. the range returned by std::views::take_exactly meets std::ranges::sized_range, independent of whether this was met by the input range.
Underlying range's reference type: The reference type is the type the elements of the underlying range are accessed by (since dereferencing an iterator or calling operator[] returns the reference type). The reference type may or may not actually contain a & (see below). For many BioC++ specific views additional concept requirements are defined for the input range's reference type, e.g. bio::views::complement can only operate on ranges whose elements are nucleotides (meet bio::alphabet::nucleotide_check). In some case the type may even be a specific type or the result of a type trait.
Returned range's reference type: Conversely certain views make guarantees on the concepts satisfied by the return range's reference type or even always have a fixed type, e.g. bio::views::complement operates on nucleotides and of course also returns nucleotides and "std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t>" would imply that the reference type is the same. However, and this is important to note, the reference type of bio::views::complement has any actual & removed from the underlying ranges' reference type (if originally present), this goes hand-in-hand with std::ranges::output_range being lost → original elements cannot be written to through this view. This is because new elements are being generated. Other views like views::reverse also preserve the & (if originally present), because the elements in the return view still point to the elements in the original range (just in different order). This has the effect that through some combinations of views you can modify the elements in the original range (if all views in the pipe preserve std::ranges::output_range), but through others you can't.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view that adds the reverse complement of every inner range in a range-of-ranges after the respective inner range.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/add_reverse_complement.hpp> This view adds the reverse complement of each inner range. The resulting output range is twice as large as the input range.
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::common_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::alphabet::nucleotide | std::remove_reference_t<std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t>> |
urng_t is the type of the range modified by this view (input).rrng_type is the type of the range returned by this view.Operating on a range of bio::alphabet::dna5:
|
inline |
A view over an alphabet, given a range of characters.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| alphabet_t | The alphabet to convert to; must satisfy bio::alphabet::alphabet. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| bio::alphabet::invalid_char_assignment | if an invalid character is encountered. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/char_strictly_to.hpp> This adaptor returns a view that transforms strings into ranges over alphabet_t.
This view differs from bio::ranges::views::char_to in that it throws an exception if an invalid character conversion happens. See bio::alphabet::assign_char_strictly_to for more details.
This view is a deep view: Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::borrowed_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::char_t<alphabet_t> | alphabet_t |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
If a range is given whose value_type is the same its alphabet type (e.g. std::string), a simple view to the range is returned and no transformation happens. See bio::ranges::views::type_reduce.
This range adaptor can be applied to ranges over bio::alphabet::cigar (although that type does not model bio::alphabet::alphabet). The returned view is weaker than in the generic case, and it is not a deep view.
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::borrowed_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | char | bio::alphabet::cigar |
Since this transformation comes with noticeable overhead anyway, this conversion is always strict, i.e. bio::views::char_to<bio::alphabet::cigar> and bio::views::char_strictly_to<bio::alphabet::cigar> are identical.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view over an alphabet, given a range of characters.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| alphabet_t | The alphabet to convert to; must satisfy bio::alphabet::alphabet. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/char_to.hpp> This adaptor returns a view that transforms strings into ranges over alphabet_t.
This view is a deep view: Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::borrowed_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::char_t<alphabet_t> | alphabet_t |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
If a range is given whose value_type is the same its alphabet type (e.g. std::string), a simple view to the range is returned and no transformation happens. See bio::ranges::views::type_reduce.
This range adaptor can be applied to ranges over bio::alphabet::cigar (although that type does not model bio::alphabet::alphabet). The returned view is weaker than in the generic case, and it is not a deep view.
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::borrowed_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | char | bio::alphabet::cigar |
Since this transformation comes with noticeable overhead anyway, this conversion is always strict, i.e. bio::views::char_to<bio::alphabet::cigar> and bio::views::char_strictly_to<bio::alphabet::cigar> are identical.
|
inline |
A view that converts a range of nucleotides to their complement.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/complement.hpp> Calls bio::alphabet::nucleotide::complement() on every element of the input range.
This view is a deep view Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::nucleotide | std::remove_reference_t<std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t>> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
| auto const bio::ranges::views::convert |
A view that converts each element in the input range (implicitly or via static_cast).
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/convert.hpp> | Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost¹ | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost¹ | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::convertible_to<out_t> | out_t |
¹ These are preserved if out_t is the same as std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t>, i.e. no conversion takes place.
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
Convert from int to bool:
Convert from bio::alphabet::dna15 to bio::alphabet::dna5:
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view that interleaves a given range into another range at regular intervals.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. |
| inserted_rng_t | The type of the range being inserted. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. |
| [in] | inserted_range | The range being inserted. |
| [in] | step_size | A value of size_t which indicates the interval to insert the inserted_range. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/interleave.hpp> This view can be used to insert one range into another range at regular intervals. It behaves essentially like | std::views::chunk(step_size) | std::views::join_with(inserted_range) (avaiable in C++23), except that it requires the underlying range and the inserted range to model std::ranges::random_access_range and std::ranges::sized_range; and that the view itself also models these concepts.
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::common_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::output_range | see below | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | see below |
The range_reference_t of the view is the common reference type of the reference types of urng_t and std::views::all_t<inserted_rng_t> const, e.g. if urange is a std::string, and inserted_range is a std::string lvalue, the reference type of this view is char &; if inserted_range is in rvalue, the reference type of this view is char const & (because of weird implementation detail of views). As a rule-of-thumb, assume that T & will turn to T const & and the output_range property is lost.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adaptor that generates all pairwise combinations of the elements of the underlying range.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/pairwise_combine.hpp> This view generates two-element tuples representing all unique combinations of the elements of the underlying range (the order of the elements is undefined). If the underlying range has less than two elements the returned range is empty, otherwise the size of the returned range corresponds to the binomial coefficient n choose 2, where n is the size of the underlying range. The reference type of this range is a tuple over the reference type of the underlying range. In order to receive the end iterator in constant time an iterator pointing to the last element of the underlying range will be cached upon construction of this view. This construction takes linear time for underlying ranges that do not model std::ranges::bidirectional_range.
The returned iterator from begin does not model Cpp17Iterator since it does not return a reference to the represented type but a prvalue. Thus this iterator might not be usable within some legacy algorithms of the STL. But it is guaranteed to work with the ranges algorithms.
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | common_tuple<std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t>, std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t>> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
Concurrent access to this view, e.g. while iterating over it, is thread-safe and must not be protected externally.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adaptor that wraps rvalue references of non-views.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/persist.hpp> For ranges that model std::ranges::viewable_range, this adaptor just returns std::views::all. However this adaptor can also take ranges that are not "viewable", e.g. temporaries of containers. It wraps them in a shared pointer internally so all view requirements like constant copy are satisfied. However construction and copying might be slightly slower, because of reference counting.
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | not required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
|
inline |
A view over an alphabet, given a range of ranks.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| alphabet_t | The alphabet to convert to; must satisfy bio::alphabet::writable_semialphabet. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/rank_to.hpp> This view is a deep view Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::rank_t<alphabet_t> | alphabet_t |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view factory that repeats a given value infinitely.
| value_t | The type of value to repeat wrapped in a std::views::single; must model std::copy_constructible. |
| [in] | value | The value to repeat. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/repeat.hpp> This view is source-only, it can only be at the beginning of a pipe of range transformations.
| Concepts and traits | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::forward_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::sized_range | |
| std::ranges::common_range | |
| std::ranges::output_range | guaranteed |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::remove_reference_t<value_t> & |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view factory that repeats a given value n times.
| value_t | The type of value to repeat; must be std::copy_constructible. |
| [in] | value | The value to repeat. |
| [in] | count | The number of times to repeat value. |
count, where each element equals value. Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/repeat_n.hpp> This view is source-only, it can only be at the beginning of a pipe of range transformations.
| Concepts and traits | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::forward_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::sized_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::common_range | |
| std::ranges::output_range | guaranteed |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::remove_reference_t<value_t> & |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adapter that decays most of the range properties and adds single pass behavior.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/single_pass_input.hpp> This view adds single-pass semantics to any input view. This means, that begin always returns the iterator to the current location in the underlying range after k elements have been already consumed and not to the begin of the underlying range, i.e. it mirrors the behavior of an input stream. Note, the view updates an internal state after moving the associated iterator. Thus, the const begin and const end are explicitly deleted.
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::common_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
Concurrent access to this view, e.g. while iterating over it, is not thread-safe and must be protected externally.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adaptor that returns a half-open interval on the underlying range.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | begin_pos | The beginning of the interval (index of first element returned). |
| [in] | end_pos | The end of the interval (index behind the last element returned). |
end_pos - begin_pos elements of the underlying range. | std::invalid_argument | If end_pos < begin_pos. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/slice.hpp> | Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
This adaptor is a combination of std::views::drop, std::views::take and bio::views::type_reduce.
If begin_pos is larger than the size of the underlying range an empty range is returned. If end_pos is larger than the size of the underlying range all elements are returned.
If end_pos < begin_pos an exception of type std::invalid_argument is thrown.
urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|
std::basic_string const & or std::basic_string_view | std::basic_string_view |
std::ranges::borrowed_range && std::ranges::sized_range && std::ranges::contiguous_range | std::span |
std::ranges::borrowed_range && std::ranges::sized_range && std::ranges::random_access_range | std::ranges::subrange |
| else | implementation defined type |
The adaptor returns exactly the type specified above.
Construction of the returned view is in 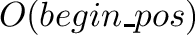
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adaptor that returns the first size elements from the underlying range (or less if the underlying range is shorter); also provides size information.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | size | The target size of the view. |
size elements of the underlying range. Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/take_exactly.hpp> | Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved except if urng_t is std::basic_string | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
The difference to bio::views::take is that this view always exposes size information – even if the underlying range is not sized. You should only use this if you know that the underlying range will always be at least size long.
For bio::views::take_exactly if the underlying range is shorter than size, the behaviour is undefined. bio::views::take_exactly_or_throw is a safer alternative, because it throws an exception when an iterator before the size-th one compares equal to the end sentinel; and it also throws on construction if it knows that the underlying range is smaller.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adaptor that returns the first size elements from the underlying range and also exposes size information; throws if the underlying range is smaller than size.
| bio::alphabet::unexpected_end_of_input | If the underlying range is smaller than size. |
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | size | The target size of the view. |
size elements of the underlying range. Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/take_exactly.hpp> | Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved except if urng_t is std::basic_string | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
The difference to bio::views::take is that this view always exposes size information – even if the underlying range is not sized. You should only use this if you know that the underlying range will always be at least size long.
For bio::views::take_exactly if the underlying range is shorter than size, the behaviour is undefined. bio::views::take_exactly_or_throw is a safer alternative, because it throws an exception when an iterator before the size-th one compares equal to the end sentinel; and it also throws on construction if it knows that the underlying range is smaller.
|
inline |
A view that calls bio::alphabet::to_char() on each element in the input range.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/to_char.hpp> This view is a deep view Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::alphabet | bio::alphabet::char_t<std::ranges::range_value_t<urng_t>> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
If a range is given whose value_type is the same its alphabet type (e.g. std::string), a simple view to the range is returned and no transformation happens. See bio::ranges::views::type_reduce.
This range adaptor can be applied to ranges over bio::alphabet::cigar (although that type does not model bio::alphabet::alphabet). The returned view is weaker than in the generic case:
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::common_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::cigar | char |
|
inline |
A view that converts each element to lower case.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/to_lower.hpp> This view is a deep view Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::meta::builtin_character | bio::alphabet::remove_reference_t<std::ranges::range_reference_t<urngt_>> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
|
inline |
A view that calls bio::alphabet::to_rank() on each element in the input range.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/to_rank.hpp> This view is a deep view Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::alphabet | bio::alphabet::rank_t<std::ranges::range_value_t<urng_t>> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
We also convert to unsigned here, because the bio::alphabet::rank_t is often uint8_t which is often implemented as unsigned char and thus will not be printed as a number by default.
|
inline |
A view that converts each element to upper case.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/to_upper.hpp> This view is a deep view Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::meta::builtin_character | bio::alphabet::remove_reference_t<std::ranges::range_reference_t<urngt_>> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adaptor similar to std::views::transform. Calls the invocable with two arguments: underlying range and position.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. |
| [in] | fn | Invocable that takes (urng_t &, size_t) as arguments and returns transformed element. |
| [in] | size_fn | Invocable that takes (urng_t &) as argument and returns size of new range. [optional] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/transform_by_pos.hpp> This view can be used to create more elaborate transformations than are possible with std::views::transform, but it only works on sized, random-access ranges.
If you want the returned range to be const-iterable, the fn that you pass should be able to handle both urng_t & and urng_t const & as arguments.
The size_fn parameter is optional; if it is omitted, the size of the returned range will be the same as the size of the underlying range. Note that the size is computed only once on construction of the returned range (and then cached).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::common_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::output_range | depends on fn | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | depends on fn | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | depends on fn | |
| std::ranges::range_value_t | std::remove_cvref_t<std::ranges::range_reference_t<rrng_t>> |
urng_t is the type of the range adapted by this view (input).rrng_t is the type of the range returned by this view.Implementation of a "reverse view":
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view that translates nucleotide into aminoacid alphabet with 1, 2, 3 or 6 frames.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. |
| [in] | tf | A value of bio::alphabet::tanslation_frames that indicates the desired frames. [optional, SIX_FRAME by default] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/translate.hpp> This view can be used to translate nucleotide sequences into aminoacid sequences (see alphabet::translation_frames for possible combination of frames).
Note that the dimension of the input is always increased by one, i.e. if you pass a single sequence, you will get multiple frames; if you pass muliple sequences, you get a as many ranges of frames.
There are also two other views for creating translations:
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::common_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::alphabet::nucleotide | std::ranges::view && std::ranges::random_access_range && std::ranges::sized_range |
urng_t is the type of the range modified by this view (input).rrng_type is the type of the range returned by this view.Operating on a range of bio::alphabet::dna5:
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view that translates nucleotide into aminoacid alphabet with 1, 2, 3 or 6 frames. Input and output range are always two-dimensional.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. Needs to be a range of ranges (two-dimensional). |
| [in] | tf | A value of bio::alphabet::tanslation_frames that indicates the desired frames. [optional, SIX_FRAME by default] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/translate_join.hpp> This view can be used to translate nucleotide sequences into aminoacid sequences (see alphabet::translation_frames for possible combination of frames). This view only operates on two-dimensional input (range of ranges) and outputs a range of ranges no matter the number of input sequences or the number of translation frames given. Therefore, it has the same capabilities as the standard view_translate but concatenates the different frames of the different input sequences rather than having a separate range for each input sequence containing the translated frames. In the output, frames are ordered in a way, that all requested frames are listed per sequence directly after each other in the order of input sequences. improved and efficient downstream post-processing if needed. However, the index of a frame for a specific sequence needs to be calculated via modulo operations in this case. The i-th frame of the j-th sequence can be calculated by n = (i * s) + j, where s is the number of frames used for translation (index starting at zero).
In short, this views behaves the same as:
There are also two other views for creating translations:
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::common_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::nucleotide | std::ranges::view && std::ranges::random_access_range && std::ranges::sized_range |
urng_t is the type of the range modified by this view (input).rrng_t is the type of the range returned by this view.Operating on a range of bio::alphabet::dna5:
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view that translates nucleotide into aminoacid alphabet for one of the six frames.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. |
| [in] | tf | A value of bio::alphabet::alphabet::translation_frames that indicates the desired frames. [optional, FWD_FRAME_0 by default] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/translate_single.hpp> This view can be used to translate nucleotide sequences into aminoacid sequences (see alphabet::translation_frames for possible frames). Note that only single frames values are are valid here.
There are also two other views for creating translations:
m frames [range → range-of-ranges OR range-of-ranges → ranges-of-ranges-of-ranges]]n sequences → n*m frames [range-of-ranges → range-of-ranges]| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::common_range | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::output_range | lost | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::alphabet::nucleotide | bio::alphabet::aa27 |
urng_t is the type of the range modified by this view (input).rrng_type is the type of the range returned by this view.Operating on a range of bio::alphabet::dna5:
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view that does quality-threshold trimming on a range of bio::alphabet::quality.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. |
| threshold_t | Either std::ranges::range_value_t<urng_t> or bio::alphabet::phred_t<std::ranges::range_value_t<urng_t>>. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | threshold | The minimum quality. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/trim_quality.hpp> This view can be used to do easy quality based trimming of sequences.
This view is a deep view Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::common_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::quality | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
Operating on a range of bio::alphabet::phred42:
Or operating on a range of bio::alphabet::dna5q:
|
inlineconstexpr |
A view adaptor that behaves like std::views::all, but type erases certain ranges.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/view_type_reduce.hpp> | Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved | |
| bio::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.
urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|
std::ranges::view | urng_t |
std::basic_string const & or std::basic_string_view | std::basic_string_view |
std::ranges::borrowed_range && std::ranges::sized_range && std::ranges::contiguous_range | std::span |
std::ranges::borrowed_range && std::ranges::sized_range && std::ranges::random_access_range | std::ranges::subrange |
| else | std::ranges::ref_view<urng_t> |
This adaptor is different from std::views::all in that it performs type erasure for some underlying ranges; std::views::all always returns std::ranges::ref_view<urng_t> or the type itself if it already is a view.
|
inline |
An identity view that throws if an encountered character is not valid for the given alphabet.
| urng_t | The type of the range being processed. See below for requirements. [template parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| alphabet_t | The alphabet to check validity for; must satisfy biocpp::alphabet::alphabet. |
| [in] | urange | The range being processed. [parameter is omitted in pipe notation] |
| bio::alphabet::invalid_char_assignment | if an invalid character is encountered. |
Header File
#include <bio/ranges/views/validate_char_for.hpp> This view throws if it encounters a character that is not in the valid set of an alphabet. It performs no transformation on the elements of the view itself. However, the contiguous property is lost due to the way it is currently implemented.
This view is a deep view. Given a range-of-range as input (as opposed to just a range), it will apply the transformation on the innermost range (instead of the outermost range).
| Concepts and traits | urng_t (underlying range type) | rrng_t (returned range type) |
|---|---|---|
| std::ranges::input_range | required | preserved |
| std::ranges::forward_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::bidirectional_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::random_access_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::contiguous_range | lost | |
| std::ranges::viewable_range | required | guaranteed |
| std::ranges::view | guaranteed | |
| std::ranges::sized_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::common_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::output_range | preserved | |
| std::semiregular | preserved | |
| biocpp::ranges::const_iterable_range | preserved | |
| std::ranges::range_reference_t | bio::alphabet::char_t<alphabet_t> | std::ranges::range_reference_t<urng_t> |
See the views submodule documentation for detailed descriptions of the view properties.